Report Materials
WHY WE DID THIS STUDY
Manufacturers with rebate agreements are required to report all of their covered outpatient drugs to the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program (Medicaid rebate program). CMS calculates rebate amounts using manufacturer reported pricing and classification data. Congress asked OIG to evaluate the accuracy of manufacturer reported data in the Medicaid rebate program, and CMS's oversight of that data. The Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) marketing categories, which also are manufacturer reported, can be used to help determine whether a drug is classified as an innovator, e.g., brand name, or noninnovator, e.g., generic, product, for the purposes of calculating Medicaid rebates. Innovator products are generally subject to higher base rebate amounts. Manufacturers are required to pay an additional, inflation adjusted rebate if a drug's price increases faster than inflation. When information provided by drug manufacturers is incorrect or missing, State Medicaid agencies may not be able to collect all appropriate rebates.
HOW WE DID THIS STUDY
We compared manufacturer reported classifications for drugs in the Medicaid rebate program to drug information in FDA files. We determined the Medicaid drug classifications that matched FDA's, and those that did not match, i.e., were potentially misclassified, in 2016. We then estimated the rebate amounts that Medicaid may have lost from 2012 to 2016 for the 10 potentially misclassified drugs with the highest total reimbursement in 2016. Finally, we reviewed CMS's policies and procedures for ensuring appropriate oversight of data submitted to the Medicaid rebate program.
WHAT WE FOUND
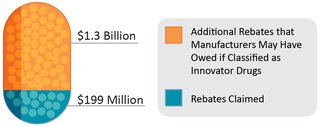
The vast majority of the approximately 30,000 drugs in the Medicaid rebate program were classified appropriately. However, we found that manufacturers may have misclassified 885 of these drugs (3 percent) in 2016. We found that from 2012 to 2016, Medicaid may have lost $1.3 billion in base and inflation adjusted rebates for 10 potentially-misclassified drugs with the highest total reimbursement in 2016.
When CMS determines that information reported by manufacturers may be incorrect, it requests that manufacturers change the data. CMS does not have the explicit legal authority to require manufacturers to change their classification data. CMS did report that when it identifies potential errors in classification data, it works with manufacturers to assist them in correcting the errors. However, CMS does not track or maintain a central database of these potential errors or their resolutions. Therefore, we had no way to determine which drugs CMS identified as potentially misclassified, or what steps, if any, CMS took to address these potential misclassifications.
Manufacturers may have owed an additional $1.3 billion for 10 potentially-misclassified drugs with the highest total reimbursement in 2016
WHAT WE RECOMMEND
We recommend that CMS (1) follow up with manufacturers associated with potentially misclassified drugs identified in this report to determine whether current classifications are correct, (2) improve its Drug Data Reporting for Medicaid System to minimize inconsistent data submissions and track potential classification errors for followup, and (3) pursue a means to compel manufacturers to correct inaccurate classification data reported to the Medicaid rebate program. CMS concurred with all three recommendations.
View in Recommendation Tracker
Notice
This report may be subject to section 5274 of the National Defense Authorization Act Fiscal Year 2023, 117 Pub. L. 263.